Back to Blog
What Is Algorithmic Trading? A Complete Guide to Automated Strategies
Learn what is algorithmic trading, how it works, and key strategies. Discover expert insights and real-world examples in our comprehensive guide.
Oct 7, 2025
generated
At its heart, algorithmic trading is just using a computer program to place a trade for you. The program follows a very specific set of instructions—rules about timing, price, or how much to buy or sell—completely automating the decision-making process.
Think of it like hiring a brilliant financial analyst who works 24/7, never gets tired, and executes trades at inhuman speeds without a single flicker of emotion. This is the technology that's quietly reshaping markets everywhere, from Wall Street to the wild world of DeFi.
From Human Insight to Automated Trades
So, how does it actually work? Algorithmic trading, or "algo trading" for short, is all about translating a human's trading strategy into a language a computer can understand and act on.
Instead of a trader staring at charts, waiting for the perfect moment to click "buy" or "sell," a pre-programmed algorithm does the watching for them. It monitors market data constantly and pulls the trigger the instant its specific conditions are met. This setup strips human emotion and second-guessing right out of the equation.
For this to happen, a few key pieces need to work together in perfect harmony. The system needs a firehose of real-time market data, a powerful computer to crunch it all, and a crystal-clear set of rules coded directly into the software. These rules can be dead simple or mind-bogglingly complex.
The Building Blocks of an Algo-Trading System
A really basic setup might follow a simple command like, "If Stock ABC's price crosses above its 50-day moving average, buy 100 shares." Easy enough.
But a more advanced system? It could be analyzing thousands of data points every second—everything from news headlines and social media sentiment to tiny price fluctuations—to inform its next move.
To give you a clearer picture, let's break down what goes into a typical algorithmic trading system.
Key Components of an Algorithmic Trading System
Component | Function | Analogy |
|---|---|---|
Trading Strategy | The brain of the operation. This is the set of rules, logic, and criteria that dictates every trade. | The game plan a coach designs before a big match. |
Coded Algorithm | The strategy translated into a programming language like Python that a computer can execute. | The recipe that turns raw ingredients into a finished dish. |
Market Data Feeds | A constant, real-time stream of information on prices, trading volume, and order books. | The live news ticker that keeps you updated on world events. |
Brokerage Connectivity | The direct link (usually an API) to an exchange or broker that allows the algorithm to place trades. | The phone line you use to call in an order to your broker. |
These components come together to create a powerful, automated trading machine.
The impact here isn't small. The global algorithmic trading market was valued at USD 21.06 billion and is on track to hit USD 42.99 billion by 2030. That growth is being fueled by big leaps in AI and an insatiable demand for faster, smarter, and more efficient ways to trade.
It’s a clear sign that automated systems are quickly becoming the new standard in finance. You can dig into more of the data on this trend over at Grand View Research.
The Blueprint for an Automated Trading Strategy
Every trading algorithm starts not with a line of code, but with a human idea. It’s the journey from a simple market observation—a spark of insight—to a fully automated system that can trade entirely on its own. This process follows a well-trodden path to turn a concept into a reliable, money-making (or money-saving) algorithm.
It all begins with Strategy Formulation. This is where a trader spots a potential edge or a recurring pattern in the market. It might be an observation as simple as, "Stocks that gap up at the open often keep running for the first hour." This core idea is the hypothesis your entire strategy will be built on.
But a vague idea isn't enough. You have to translate it into a rigid, non-negotiable set of rules. For instance, our "gap up" idea could be broken down like this:
Entry signal: Buy a stock if its opening price is 2% higher than the previous day's close.
Exit signal (Profit): Sell if the price jumps 1% from where you bought it.
Exit signal (Loss): Get out if the price drops 0.5% below your entry point.
Time constraint: No matter what, close the position after 60 minutes.
Rules this precise remove all emotion and guesswork. They create a clean blueprint that a computer can understand and execute flawlessly.
From Rules to Reality
Next up is the Coding and Backtesting phase. This is where a developer, or a trader who can code, translates those rules into a language like Python. The abstract strategy is now a real piece of software that can analyze data and pull the trigger on trades.
The real test, though, is backtesting. This is a critical simulation where you unleash your new algorithm on historical market data to see how it would have performed in the past. It’s like a dress rehearsal for the live markets, and it will mercilessly expose your strategy's strengths and fatal flaws without you having to risk a single dollar.
Backtesting is where you ask the hard questions: Is this thing actually profitable? How much risk does it take? Does it only work when the market is trending up? A solid backtest is probably the single most important step in figuring out if you've got a winner.
The infographic below gives a bird's-eye view of how an algorithm processes information to execute a trade.
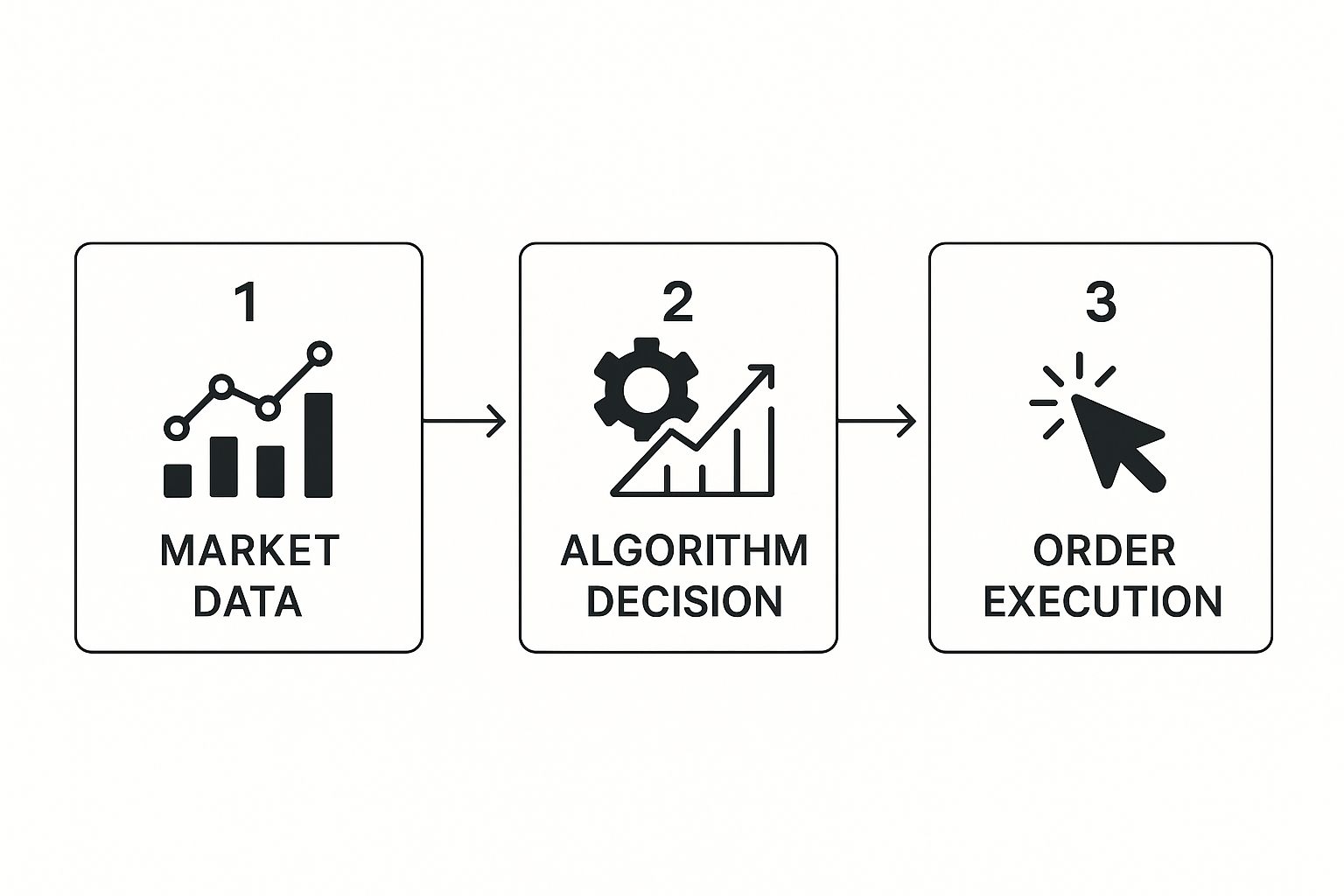
As you can see, it's a powerful, straightforward loop: the algorithm gets market data, runs it through its rules, and fires off an order.
Deployment and Live Trading
Once a strategy survives the rigors of backtesting and refinement, it's time for Deployment. The algorithm gets connected to a live brokerage account through an API (Application Programming Interface), which lets it see real-time market data and send orders automatically.
How quickly your system gets and processes that data can make or break a strategy. Understanding the intricacies of real-time data streaming is non-negotiable if you want to build high-performance bots.
Some of the more advanced strategies go even further, weaving in complex predictive models. You can get a feel for how developers are building powerful machine learning trading algorithms in our deep-dive guide on the topic. From this point on, the algorithm is on its own—monitoring the market and trading based on its programming, turning that initial spark of an idea into an active participant in the market.
Common Algorithmic Trading Strategies Explained

Not all trading algorithms are created equal. Far from it. They’re actually purpose-built tools, each designed to execute a very specific game plan based on a particular view of how markets work.
Getting a handle on the logic behind these game plans is the key to understanding what algorithmic trading is all about. While the variations are nearly endless, most strategies fall into a few core categories.
Riding the Wave with Trend-Following
One of the most intuitive approaches is Trend-Following. These algorithms operate on a simple, timeless premise: an asset in motion tends to stay in motion.
Think of it like a surfer catching a wave. The algorithm's job is to spot a good wave forming (an uptrend), get on it (buy), and then ride it for as long as possible before it breaks (the trend reverses). The code is built to identify and ride market momentum, buying assets that are consistently climbing and selling (or shorting) those in a clear downtrend.
Hunting for Price Gaps with Arbitrage
Another powerful strategy is Arbitrage, which is all about exploiting tiny, fleeting price differences for the same exact asset across different markets. It's a game of pure speed.
For example, a stock might be trading for $100.01 on the New York Stock Exchange but $100.00 on another exchange at the very same instant.
An arbitrage algorithm is programmed to spot this microscopic discrepancy instantly. It would simultaneously buy the stock on the cheaper exchange and sell it on the more expensive one, locking in a virtually risk-free profit of one cent per share. It might not sound like much, but when you do this thousands of times a second with huge volumes, those tiny profits add up very, very quickly.
At its core, arbitrage is a race. The first algorithm to spot and act on a price difference gets the reward, which is why speed and low-latency connections are absolutely critical for this type of strategy.
Betting on the Rebound with Mean Reversion
In direct contrast to trend-following, Mean Reversion strategies are built on the idea that prices eventually snap back to their historical average, or "mean." These algorithms are constantly on the lookout for assets that have stretched too far in one direction, becoming overbought or oversold, and they bet on the inevitable return to normal.
Imagine a pendulum. No matter how far it swings to one side, gravity always pulls it back toward the center. A mean reversion algorithm identifies when the pendulum has swung to an extreme and places a trade in the opposite direction, anticipating its journey back to the middle.
This approach requires some serious statistical analysis of an asset's past behavior to figure out what "normal" even looks like.
To give you a clearer picture, let's break down how these different strategies stack up against each other.
Comparing Popular Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Strategy Type | Core Logic | Typical Timeframe | Best Market Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
Trend-Following | "The trend is your friend." Buy high, sell higher. | Medium to Long-Term | Strong, directional markets (bull or bear). |
Mean Reversion | "What goes up, must come down." Buy low, sell high. | Short to Medium-Term | Ranging or sideways markets with volatility. |
Arbitrage | Exploit price differences for the same asset. | Ultra Short-Term (milliseconds) | Any market with multiple trading venues. |
As you can see, each strategy has its own unique fingerprint—a specific logic, timeframe, and ideal environment where it thrives. This is just a glimpse into a much larger world of automated approaches.
Each of these concepts offers a unique way to tackle the markets, and you can explore more of the best automated trading strategies in our detailed guide.
The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly of Automated Trading
Algorithmic trading gives you an edge, letting you operate at a speed and scale that’s flat-out impossible for a human. But that power is a double-edged sword. It comes with its own unique and pretty significant risks. Getting a handle on both sides of this coin is a must before you even think about diving in.
The advantages are hard to ignore. Algorithms can execute trades at lightning speed with perfect precision, jumping on opportunities that are gone in the blink of an eye. They also get rid of the emotional baggage—fear, greed, hesitation—that trips up so many human traders. Every move is based purely on data and the logic you set, nothing else.
Even better, one of the biggest wins is the ability to rigorously backtest a trading idea. Before you risk a single dollar, you can run your strategy against years of historical market data. This gives you a massive head start in understanding its potential and where the weak spots might be.
The Upside of Automation
The benefits make it pretty clear why so many traders are turning to automated systems.
Warp Speed Execution: An algorithm can chew through market data and place an order in microseconds. No human can even come close.
Zero Emotional Baggage: By sticking to a strict set of rules, bots avoid those gut-reaction trades driven by market panic or a sudden rush of greed.
Test Before You Invest: You can simulate how your strategy would have performed in past market conditions to fine-tune it and set realistic expectations. This is the power of backtesting.
Scale Like Crazy: A single algorithm can watch hundreds of markets or assets at once, working 24/7 without ever getting tired.
Put it all together, and you have a recipe for a highly disciplined and efficient way to trade.
The Dangers Lurking in the Code
As great as that sounds, the risks are just as real. A tiny bug in your code or a bad assumption in your strategy’s logic can lead to catastrophic losses in seconds. The very speed that makes algorithms so effective can also magnify the damage from a mistake long before a human can hit the kill switch.
Another huge pitfall is over-optimization, which is sometimes called "curve fitting." This is what happens when you tweak a strategy so much that it works perfectly on past data but completely falls apart in a live market. Your model has basically just memorized the past instead of learning principles that can adapt to the future.
The biggest risk in algorithmic trading isn't a market crash—it's a flawed model. A system that looks perfect on paper can turn into a wealth-destroying machine if its logic is wrong or it can't handle new market behavior.
Even the tech behind these systems can cause headaches. The algorithmic trading market is a mixed bag, with traders choosing between flexible cloud setups or high-control systems they run themselves. While the cloud is popular because it's cheaper, the constant threat of data breaches is a serious concern for any automated strategy. A report from Coherent Market Insights dives deeper into these deployment trends and what's driving the market.
At the end of the day, algorithmic trading is not a "set it and forget it" magic button. It demands constant attention, ongoing tweaks, and a deep understanding of both the markets and the technology making the trades happen.
Algorithmic Trading in the Real World
So where does all this theory hit the pavement? Beyond the code and concepts, these automated systems are the invisible engines powering a massive chunk of modern financial markets. They're working behind the scenes in all sorts of ways, from quietly filling huge institutional orders to providing the essential liquidity that keeps everything flowing smoothly.
One of the most common jobs for trading algos is helping out the big players, like pension funds or mutual funds. Imagine a fund needs to buy millions of shares of a single stock. If they just dropped one massive order onto the market, the price would skyrocket instantly, giving them a terrible entry point.
That's where they bring in the bots. Using clever techniques like smart order routing, these algorithms slice that massive order into thousands of tiny, strategically timed pieces. They then execute these micro-trades across different exchanges to avoid making a splash, ensuring the fund gets the best possible average price without tipping its hand. It's a stealth operation, pure and simple.
Powering Market Liquidity
Another critical role for algorithmic trading is market making. Think of market-making algorithms as the grease in the gears of an exchange. They provide liquidity by constantly placing both buy and sell orders for a particular asset, creating a two-sided market.
This ensures there’s almost always someone on the other side of your trade. By pocketing the tiny difference between the buy and sell price (the "spread"), these bots make trading more efficient for everyone else. Without them, markets would be far more sluggish, making it harder and more expensive to move in and out of positions quickly.
The global shift to these automated systems is impossible to ignore. While North America has been the long-standing giant in the algorithmic trading market, countries across Asia Pacific are now pouring money into the technology to boost their own trading efficiency. It’s a clear signal of a worldwide trend. You can get more details from this algorithmic trading market analysis.
The New Frontier in Decentralized Finance
It's no surprise that algorithmic trading has found a natural home in the wild, fast-paced world of Decentralized Finance (DeFi). In this permissionless ecosystem, trading bots run 24/7, hunting for opportunities that a human trader could never hope to catch.
They pull off complex arbitrage trades between different decentralized exchanges in the blink of an eye and automate sophisticated yield farming strategies to squeeze every last drop of return from digital assets. These bots aren't just a nice-to-have; they're essential to the very function and efficiency of the DeFi space. As the tech gets smarter, more and more traders are turning to the best AI trading platforms to find their edge.
What's Next for Algorithmic Trading?
So, we've seen how algorithmic trading has grown from a specialized tool for big institutions into a core part of modern finance. We've walked through how strategies are built, weighed the incredible speed against the serious risks, and looked at its impact everywhere from Wall Street to the world of DeFi.
But the big question is, where does it go from here?
The future of algo trading is all about artificial intelligence and machine learning. The bots of tomorrow won't just blindly follow the rules we give them. They'll actually learn on the fly.
Imagine an algorithm that can sense a subtle shift in market sentiment before anyone else notices, and then rewrites its own strategy to get ahead of the curve. That's where we're headed.
The next big leap in trading isn't just about being faster; it's about being smarter. Algorithms that can learn, predict, and fix their own mistakes will run the markets of the next decade.
This isn't some far-off sci-fi concept, either. It's already starting to happen. Top financial firms are pouring resources into AI that can not only execute trades better but can dream up entirely new strategies—ones a human might never even think of.
As this tech gets easier to access, understanding the basics of how these systems work will be a must for anyone serious about the markets. It's no longer just a game for massive hedge funds. The era of the self-improving trading bot has just kicked off.
Your Algo Trading Questions, Answered
Jumping into algorithmic trading always brings up a few key questions. It's a big topic, after all. Let's walk through the common ones to clear things up and give you a practical sense of what it takes to get started.
Do I Need to Be a Coder to Do This?
Not anymore. While knowing a language like Python gives you the ultimate freedom to build completely custom strategies from scratch, it's definitely not the only path. The space is now filled with no-code and low-code platforms that let you design and launch trading bots with simple, visual tools.
Think of it like building a website. Years ago, you had to be a pro at HTML and CSS. Now, tools like Squarespace let you drag and drop your way to a beautiful site. No-code trading platforms work the same way; you connect logical blocks—like "if the price of ETH crosses above its 50-day moving average, then buy"—without writing a single line of code.
This is a fantastic way for beginners to get their feet wet. You can test your trading ideas and learn the core principles of strategy design firsthand. You might give up some deep customization, but for ease of use and as an entry point, it's a brilliant way to understand how algorithmic trading works in practice.
Is Algorithmic Trading Actually Legal?
Yes, algorithmic trading is perfectly legal and is a massive part of most major financial markets, including in the United States. But it’s not the wild west. The whole industry is watched over by regulatory bodies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
These rules are in place to stop market manipulation, keep pricing fair, and make sure it's a level playing field for everyone. Sneaky tactics like "spoofing"—placing huge orders you never intend to fill just to spook the market—are totally illegal.
The big takeaway here is that while the technology itself is legal, what you do with it is what matters. The best way to stay on the right side of the law is to always work with a reputable, regulated broker. That way, you know you're playing by the rules and your money is safe.
How Much Money Do I Need to Start Trading with Algorithms?
This is probably the most common question, and the honest answer is: it depends. There's no single magic number to get started. Your starting capital could be anything from a few hundred dollars to millions.
For a regular trader just starting out, you can absolutely begin with a small account—sometimes as little as $100 to $500. This is especially true if you're using accessible platforms and trading in markets with lower costs, like crypto or forex. The golden rule is to start small and only put in what you can genuinely afford to lose.
Think of your first pot of money as your "tuition fee." You're paying to learn, to test your strategies, and to make mistakes without it being a financial disaster. Once you get the hang of it and build some confidence, you can think about adding more capital. The initial focus should always be on smart risk management, not on trying to get rich overnight.
Ready to put your stablecoins to work without the steep learning curve? Yield Seeker uses a personalized AI Agent to find and manage the best yield opportunities in DeFi for you. Start earning passive income safely and automatically. Discover how it works at https://yieldseeker.xyz.
